Deep Tech Briefing #26: 🌠 Silicon Quantum Leap; 🚛 AI Boosts Military Supply Chains; 🍗 Cost-Effective Cultivated Meat Manufactoring; 🪐 Next Frontier in Asteroid Mining and more...
An insider’s update on Deep Tech Ventures: Your dose of tech innovations, startups, exponential industries, policies, and market moves to stay ahead and capitalize on it.
Hey there! Welcome to this edition of Deep Tech Briefing, our Sunday column where we break down the week’s top developments in Deep Tech Startups and Venture Capital.
Subscribe for free to get it straight to your inbox every Sunday, and read it whenever you like!
In today’s edition
Major breakthroughs in quantum computing drive silicon-based advancements
Military logistics gets a strategic AI upgrade with significant seed funding
Cultivated meat production nears cost parity with conventional products
Asteroid mining company sets sights on a third deep space mission
Holographic display technology edges closer to mainstream consumer devices
✨ For more, see Membership | Partnership | Deep Tech Catalyst
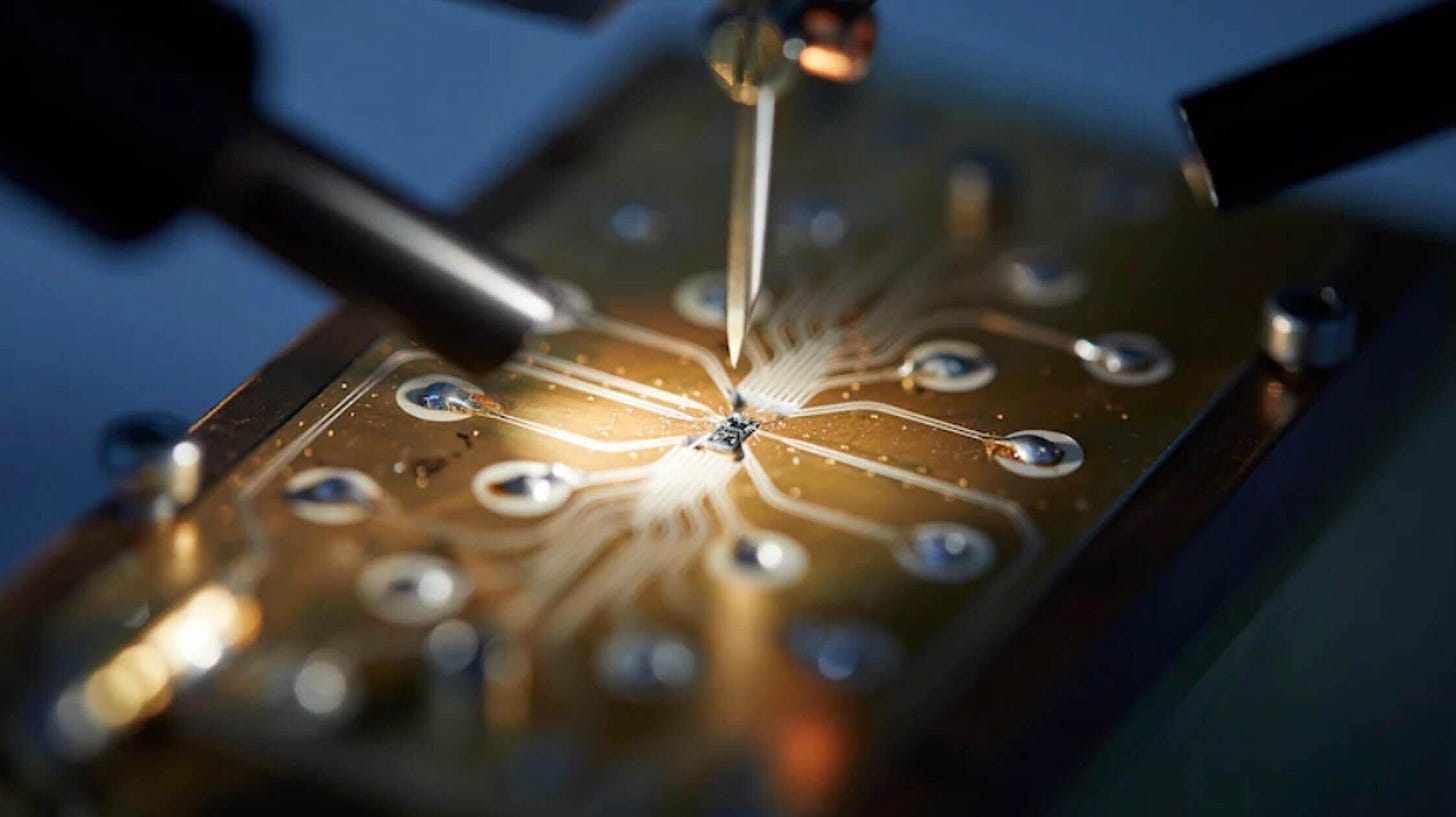
🔸 Silicon-Based Quantum Computing: A Pivotal Advance in the Global Quantum Race
“Two-qubit gate accuracy in CMOS to above 99%” - Diraq on LinkedIn
A big challenge in quantum computing lies in maintaining the coherence and reliability of qubits over time. Qubits, the fundamental building blocks of quantum information, are exceedingly sensitive to environmental noise, temperature fluctuations, and other disturbances, leading to error-prone quantum operations. For quantum computers to be practically useful, these errors must be mitigated, necessitating the development of fault-tolerant quantum systems—systems that operate accurately despite errors.
Fault tolerance requires qubits with exceptionally high fidelity—typically above 99%—to perform reliable quantum operations. However, consistently achieving this level of fidelity across millions or billions of qubits has proven to be a significant obstacle. For instance, superconducting qubits, one of the leading quantum technologies, require ultra-cold temperatures and specialized infrastructure, making it technically and economically challenging to scale beyond a few thousand qubits. However, the goal is that quantum computers must scale to millions or eventually billions of qubits, and if managing even a small number of qubits is a big challenge, the task of controlling billions is exponentially more difficult.
Founded by Professor Andrew Dzurak, Diraq, an Australian quantum computing startup, has made strides in this area by developing qubits using silicon-metal-oxide-semiconductor (SiMOS) technology. On Tuesday, the quantum startup announced a technological breakthrough in Nature Physics, demonstrating consistent and repeatable two-qubit gate operations with fidelity above 99% on the SiMOS quantum dot platform.
Central to Diraq's innovation is the use of SiMOS quantum dots. These quantum dots are essentially modified transistors designed to function as qubits. In a SiMOS system, individual electrons are confined within a tiny region of silicon, known as a quantum dot. The spin of these electrons is then manipulated to represent quantum information. By shrinking transistor sizes to the quantum scale, Diraq can control these individual electrons with high precision, allowing them to function as qubits.
"The major advantage of the technology Diraq is working on is that we have the potential to realize millions of qubits because we utilize standard integrated circuit technology," explains Professor Andrew Dzurak, CEO of Diraq.
This breakthrough is particularly significant because it aligns quantum computing with the existing semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem. The compatibility of the technology with complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) processes means that scaling up to millions, or even billions, of qubits is theoretically feasible using current manufacturing methods. This is in stark contrast to other platforms, such as superconducting qubits, which face substantial technical and economic challenges when scaled beyond a few thousand qubits. For example, maintaining quantum entanglement across a broad range of superconducting qubits requires complex cooling systems and infrastructure that are prohibitive in terms of both space and cost.
Looking ahead, quantum computing is poised to revolutionize multiple industries by solving problems currently intractable for classical computers. In the pharmaceutical sector, for example, quantum computers could model complex molecules to accelerate drug discovery, while in finance, they could optimize portfolios or simulate market dynamics with unprecedented precision. In fact, the global quantum computing market is expected to grow over $6.6 billion by 2033, reflecting significant investments in scaling quantum systems to meet real-world demands.
🔸A Multi-Million Dollar Seed Round to Advance AI in Tackling Military Logistics' Challenges
In military operations, logistics remains a critical yet complex challenge, and "Despite the complexity behind military operations, leaders currently rely on whiteboards and Excel spreadsheets to map out logistics. [...] Today, total DoD spend on software is less than 1% of its total ~$850 billion budget, meaning software penetration is still only in its early days." - Bessemer Venture Partners
These limitations have often led to inefficiencies, delays, and increased risks in supply chain management. The emergence of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and predictive analytics is transforming the landscape of military logistics.
These technologies offer substantial improvements over traditional methods by enabling real-time decision-making, optimizing supply chain processes, and enhancing the resilience of logistics networks against potential disruptions.
A notable example of this is the use of AI-based systems by the U.S. Army, which leverages IBM’s Watson to manage logistics data in the cloud, thereby improving efficiency and reducing the workload of analysts.
Recognizing this, DEFCON AI is experimenting with an innovative approach to military logistics and strategic planning through